Overview
This R package assists breeders in linking data systems with their analytic pipelines, a crucial step in digitizing breeding processes. It supports querying and retrieving phenotypic and genotypic data from systems like EBS, BMS, BreedBase, and GIGWA (using BrAPI calls). Extra helper functions support environmental data sources, including TerraClimate and FAO HWSDv2 soil database.
Author and Maintainer: Khaled Al-Shamaa <k.el-shamaa (at) cgiar (dot) org>
Contributor: Mariano Omar CRIMI <m.crimi (at) cgiar (dot) org>
Contributor: Zakaria Kehel <z.kehel (at) cgiar (dot) org>
Contributor: Johan Aparicio <j.aparicio (at) cgiar (dot) org>
Copyright Holder: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
BrAPI
The Breeding API (BrAPI) project is an effort to enable interoperability among plant breeding databases. BrAPI is a standardized RESTful web service API specification for communicating plant breeding data. This community driven standard is free to be used by anyone interested in plant breeding data management.
Supported Data Sources
-
BMS:
vignette("bms_example"). -
EBS:
vignette("ebs_example"). -
Breedbase:
vignette("breedbase_example"). -
GIGWA:
vignette("gigwa_example").
Extra sub-systems supported:
Installation
install.packages("QBMS")Development version
To get a bug fix or to use a feature from the development version, you can install the development version of QBMS from GitHub.
if (!require("remotes")) install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("icarda-git/QBMS")Getting Started
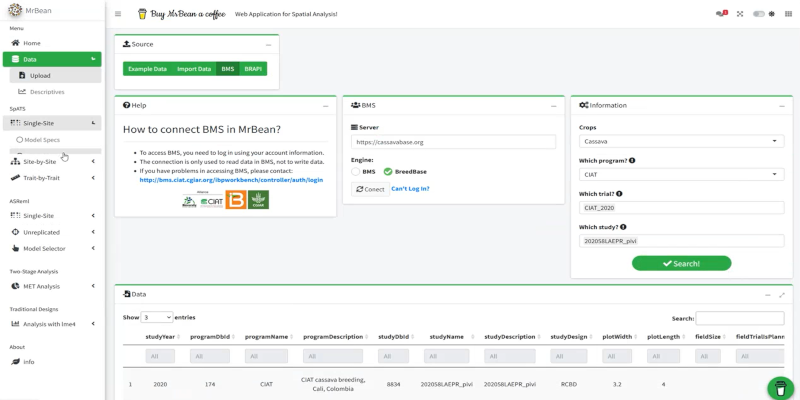
Once you successfully install the QBMS R package, you can load it as a library and set up your remote server configuration (e.g., EBS, BMS, BreedBase, or GIGWA) by simply copying and pasting the login page URL from your web browser.
# load the QBMS library
library(QBMS)
# config your BMS connection (by providing your BMS login page URL)
set_qbms_config("https://bms.icarda.org/ibpworkbench/controller/auth/login")To start querying and retrieving data from your remote server, you have to login using the same credentials for that server’s GUI/web interface. Please note that you can call the login function(s) with no parameters (interactive mode), where you will get a popup window to insert your username and password (highly advised as one of the best security practices). Although, for automatic analysis pipeline(s) or server services, you can still provide the required username and password as login function parameters (i.e., batch mode).
# login using your account (interactive mode)
login_bms()
# or pass your username and password as parameters (batch mode)
login_bms("username", "password")You should be careful when sharing your batch mode code to avoid leaking your credential in public or not authorized spaces.
Boosting Big Queries Performance
You can get benefit from an external suggested R package (not on CRAN yet) named async to improve the performance of multi-page API calls by optionally enabling asynchronous calls to prevent blocking behavior by fetching all requested pages simultaneously (this helps to reduce the waiting time for the user).
All that you need to do to activate this option is to install the async package manually using the following line of code, and QBMS will take care of the rest ;-)
remotes::install_github("r-lib/async")Supporting Multiple Provider Connectors
You can switch between an ongoing QBMS connection and another server/database connection by using get_qbms_connection() and set_qbms_connection() functions, as shown in the following example (i.e., if there is a need to switch forth and back during the same session):
# configure QBMS to connect the phenotypics server
set_qbms_config("https://www.bms-uat-test.net/ibpworkbench/controller/auth/login")
# login and retrieve data from the phenotypic server
# save current connection (phenotypic server)
con1 <- get_qbms_connection()
# configure QBMS to connect the genotypic server
set_qbms_config("https://gigwa.southgreen.fr/gigwa/", engine = "gigwa", no_auth = TRUE)
# retrieve data from the genotypic server
# save current connection (before switch)
con2 <- get_qbms_connection()
# load the saved phenotypic server connection
set_qbms_connection(con1)
# continue retrieving data from the phenotypic serverA detailed example is available in the documentation of the
get_qbms_connection()andset_qbms_connection()functions.
Also, you can find a more elegant solution developed by Francisco Agosto-Perez from the Breeding Informatics team within the Innovation Lab For Crop Improvement at Cornell University available here: https://github.com/agostof/BrAPI-Provider/
Error and Debugging
If you get unexpected results or weird behavior and want to dig deep and investigate what went wrong, you can get a copy of the internal QBMS variables by calling the debug_qbms() function.
dump <- debug_qbms()
dump$config
# $crop
# [1] "maize"
#
# $server
# [1] "https://www.bms-uat-test.net"
#
# $path
# [1] "bmsapi"
#
# $page_size
# [1] 1000
#
# $time_out
# [1] 120
#
# $base_url
# [1] "https://www.bms-uat-test.net/bmsapi"
#
# $engine
# [1] "bms"
names(dump$state)
# [1] "token" "program_db_id" "trial_db_id" "study_db_id" "user"
# [6] "expires_in" "errors" ...
dump$state$token
# [1] "username:1666907125029:a312bb036cc8d9cc302bee1f0981e5ab"Troubleshooting the Installation
If the installation of QBMS generates errors saying that some of the existing packages cannot be removed, you can try to quit any R session, and try to start R in administrator (Windows) or SUDO mode (Linux/Ubuntu) then try installing again.
If you get an error related to packages built under a current version of R, and updating your packages doesn’t help, you can consider overriding the error with the following code. Note: This might help you install QBMS but may result in other problems. If possible, it’s best to resolve the errors rather than ignoring them.
Sys.setenv("R_REMOTES_NO_ERRORS_FROM_WARNINGS" = TRUE)
remotes::install_github("icarda-git/QBMS", upgrade = "always")- If you get an error related to list or set runs in GIGWA (i.e.,
gigwa_list_runs()andgigwa_set_run()functions), you can try to ensure that your R session system locale is using UTF-8 character set encoding. You may consider overwriting your system locale with the following command to resolve this issue:
Sys.setlocale("LC_ALL", "English_United States.utf8")- If you get the following error message:
'synchronise' is not an exported object from 'namespace:async', then double-check that you have installed the correctasyncpackage we recommended. Users may encounter this error because they installed a differentasyncpackage from the CRAN repository! Please uninstall it before installing the required R package from Github (for more details, please refer to this GitHub issue):
remove.packages("async")
if("package:async" %in% search()) detach("package:async", unload = TRUE)
remotes::install_github("r-lib/async")- If the
get_terraclimate()function takes a long time to run and the progress bar stays at 0%, it might be due to using an outdated version of the R language. Make sure you’re using the latest version. For more details, please refer to this GitHub issue.
References
Peter Selby et al., BrAPI-an application programming interface for plant breeding applications, Bioinformatics, Volume 35, Issue 20, 15 October 2019, Pages 4147–4155, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz190
The Breeding API (2022, December 15). BrAPI Compatible Software list. Retrieved from https://brapi.org/compatibleSoftware
Excellence in Breeding Toolbox (2023, February 1). Query Breeding Management Systems (QBMS) R package. Retrieved from https://excellenceinbreeding.org/toolbox/tools/query-breeding-management-systems-qbms-r-package
CGSpace (2023, February 23). Query Breeding Management Systems (QBMS) R package. Retrieved from https://cgspace.cgiar.org/handle/10568/128828
MELSpace (2023, February 23). Query Breeding Management Systems (QBMS) R package. Retrieved from https://repo.mel.cgiar.org/handle/20.500.11766/68139
